


Welltory is the Ultimate HRV App





Sleep is as important for your health as food, water, and oxygen. Sleep aupports all kinds of vital processes including your cognitive abilities, your autonomic nervous system, metabolism, and immune system, for starters. Inversely, science suggests that not getting enough quality shut eye can increase the risk for high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression.
To understand how and why sleep impacts your health, you’ll need to dive into the various stages of sleep that you cycle through each night.
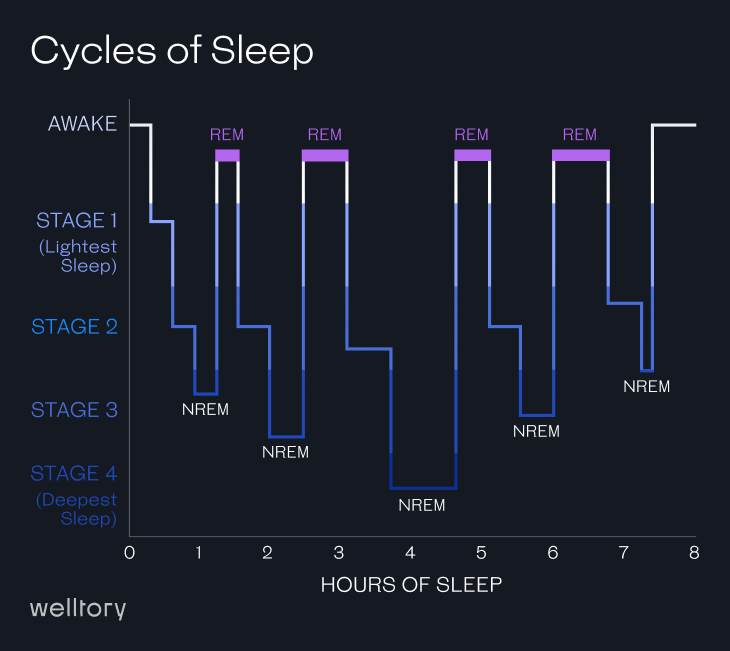
While you sleep, your body cycles through four stages of sleep, with each cycle lasting about 90-110 minutes. If they’re getting the recommended 7 to 9 hours of sleep, a person should go through 4-6 cycles per night.
The four stages of sleep include 3 stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and 1 stage of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. These categorizations are based on the brain and body activity during sleep.
The time spent in each sleep stage changes as we age. The amount of sleep you need also decreases with age.
We are different and so are our sleep cycles: they vary night to night based on a wide range of factors such as age, recent sleep patterns, stress, and food and drink consumption. Here you can find a caffeine intake simulator that will show you when you can expect restful sleep.
Men tend to spend more time in light sleep and experience more awakenings throughout the night, and more daytime sleepiness as a result. Women stay longer in slow-wave sleep but experience difficulty falling asleep more often than men. For women, daytime sleepiness usually increases during pregnancy and for the first few months of postpartum.
This is the lightest and shortest stage of sleep that lasts 5 to 10 minutes on average. Muscle tone is still present in the skeletal muscles. Breathing occurs at a regular rate. It’s the easiest to wake up.
This stage lasts for about 20 minutes. The sleeper is less able to be awakened in comparison to stage 1 but it’s still easy to wake them up. This is why naps should be less than 30 minutes to avoid waking during deep sleep. Waking up when you are in the deepest stage of sleep can cause sleep inertia, which results in impaired performance and grogginess. This is particularly important for people performing safety-critical tasks that take naps during work, for example, medical personnel working night shifts. In the US, 100,000 deaths occur annually in hospitals due to medical errors, where sleep deprivation of staff makes a significant contribution.
Get Welltory
for better sleep
Get Welltory
for better sleep

Deep sleep takes about 20-40 minutes. When you are in SWS it is more difficult to wake you up. American Sleep Association claims that even very loud noises over 100 decibels might not wake a person up during deep sleep.
Harvard Medical School suggests that many physiological activities are reduced during sleep, for example, kidney function slows down and the production of urine is decreased. However, there are physiological processes that increase during sleep. Your pituitary gland sends out human growth hormone, which is vital for kids to grow bones and for everyone to repair muscle and other tissue.
Deep sleep is also important for glucose regulation in adults. Studies show that a lack of good night sleep can lower your insulin sensitivity meaning you will feel hungrier and eat more. People who sleep less than seven hours per night are more likely to develop obesity than those who sleep more and the risk of diabetes also increases with too little sleep.
Experts think that sleep jump-starts your immune system. When you have an infection, you get more deep sleep to get better faster.
In terms of brain activity, the stage of REM sleep is associated with dreaming and is similar to being awake. The heart rate can increase, breathing becomes more irregular but the skeletal muscles are still atonic. It’s believed that the first period of REM lasts 10 minutes. Each of your later REM stages gets longer, and the final one may last up to an hour. During REM, the brain is highly active, increasing brain metabolism by up to 20%.
Behavioral and neurophysiological evidence supports the role of REM sleep for amygdala-related memory processing: the amygdala-hippocampus-medial prefrontal cortex network involved in emotional processing, fear memory, and valence consolidation shows the strongest activity during REM.
The order of sleep stages is following: Falling Asleep, Light Sleep, Slow Wave Sleep, sometimes called the deepest sleep, and REM sleep – dreaming stage. Some smartwatches will also show you times when you are awake as part of the cycle. Each stage of sleep includes variations in muscle tone, brain wave patterns, and eye movements.
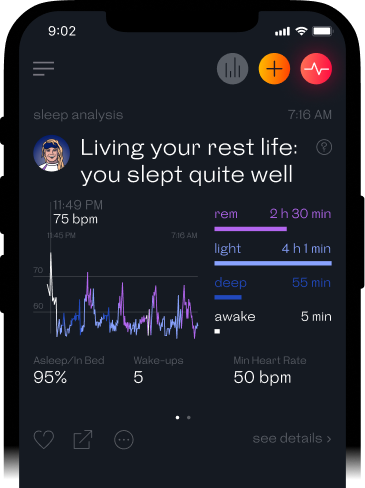
You can track stages of your own sleep with Welltory
Researchers are still exploring the purpose of the different stages of sleep, and the impact they have on our bodies. What is known is that the quality and time spent in each sleep stage may be affected by depression, aging, traumatic brain injuries, medications, and circadian rhythm disorders.
Each sleep stage has its own function. Light sleep is important for memory, learning, and motor skills. During deep sleep, your body recovers, grows, and regulates its internal processes.
When you don’t get enough deep sleep, your body has a harder time fighting infections and forming an immune response. Moreover, without deep sleep, toxins that build in your brain while you are awake do not get flushed out. This increases the risk of health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases.
REM sleep stimulates areas of your brain that are central to learning, making memories, and cognitive function. This is when the brain exercises important neural connections that are key to mental and physical health. Behavioral and neurophysiological evidence supports the role of REM sleep for amygdala-related memory processing: the amygdala-hippocampus-medial prefrontal cortex network involved in emotional processing, fear memory, and valence consolidation shows the strongest activity during REM.
Experiencing too much stress (good or bad) can increase the intensity and length of REM sleep and, thus, reduce the deep sleep that your body needs to repair. It’s advised to meditate, take hot baths, and try to calm down before going to sleep to promote more slow wave sleep.
Understanding what happens during every stage of your body provides helpful insights into your overall health. More and more research is being done on sleep as the so-called “epidemic” of sleep deprivation is rising. Sleep loss and sleep disorders are among the most common yet frequently overlooked health problems.
You can start improving your sleep quality and quantity with Welltory’s SBQ clinical test to find if your sleep habits are putting you at risk of developing a wide range of negative health consequences such as cardiovascular problems, increased risk of obesity, and mental health problems like excessed stress, depression, and anxiety.
To improve the quality of your sleep you can start monitoring and analyzing how long you sleep and how your body systems work during your sleep. Pulse monitoring is one of the most accurate methods to track your sleep.
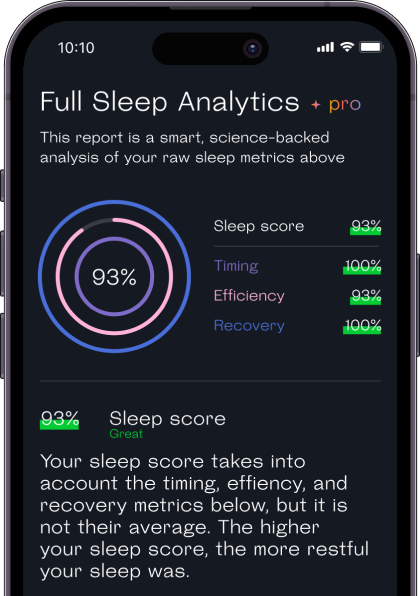
Welltory uses data such as heart rate and heart rate variability from your sleep tracker or a smartwatch that takes into account 3 smart sleep metrics — Timing, Efficiency, and Recovery. Our algorithm adapts to you over time and uses your historical sleep data.
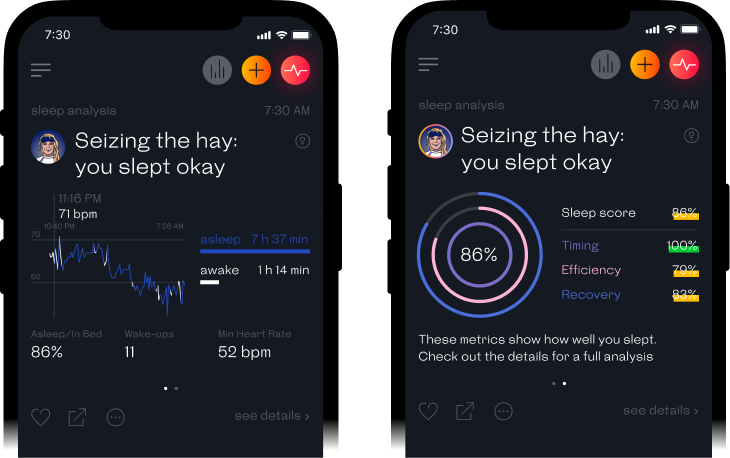
Tracking your sleep can help you determine the amount of time you are asleep by analyzing changes in your physical activity, including movement during the night. Getting enough sleep is important for health-promoting activities like digestion, growth, and memory. The best thing you can do to improve your sleep quality is to work on your sleep hygiene.
Welltory Team, 27 Jan. 2023
 App Store
App Store
 Google Play
Google Play
 Huawei AppGallery
Huawei AppGallery
 Galaxy Store
Galaxy Store

