


Welltory is the Ultimate HRV App





When the sun sets and the day winds down, many of us feel the familiar pangs of hunger creeping in. The question arises: Is it a good idea to indulge in a late-night snack before heading to bed? The topic of eating before bedtime has sparked numerous debates, with conflicting opinions and myths circulating widely. Lets delve into the scientific research surrounding eating before bed to shed light on its effects on sleep, digestion, weight management, and overall health.
Numerous studies have investigated the potential effects of eating before bedtime on sleep. While some early research suggested a negative correlation between the two, more recent and rigorous studies have shown that moderate, mindful late-night snacking may not significantly disrupt sleep quality or duration. The key lies in the choice of foods and portion sizes.
Certain foods, such as fried foods, cheeseburgers, and spicy curries, can lead to discomfort and disruptions in sleep because of their high calorie, fat, and spice content. Such foods may promote acid reflux and heartburn, causing frequent awakenings during the night.
A 2005 study published in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology found that high-fat diets may be associated with a decrease in total sleep duration. Additionally, spicy foods can cause heartburn, particularly if consumed shortly before bedtime. Acid reflux and heartburn at night have been linked to certain foods in numerous studies.
On the other hand, lighter snacks like whole grain crackers, bananas (which have serotonin-boosting properties), or a cup of milk (rich in protein) can have a positive effect on sleep. These snacks may help induce relaxation and ease the transition into deep sleep.
Additionally, the timing of meals plays a role in sleep quality. For instance, indulging in a big steak dinner or a heavy pasta dish right before bedtime might hinder relaxation. Instead, aiming for a moderate, balanced meal like a chicken salad or a bowl of vegetable soup a few hours before sleeping can potentially enhance sleep quality.
Melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles, is affected by our eating habits. Emerging evidence suggests that consuming certain foods high in tryptophan, such as nuts and seeds, may aid in melatonin production, potentially promoting better sleep when consumed before bed.
Tryptophan itself is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in the production of serotonin, which can be converted to melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. Melatonin production is influenced by a combination of dietary tryptophan intake and exposure to light, especially darkness.
Studies have shown that dietary intake of tryptophan can influence brain levels of serotonin. Conversely, consuming foods high in tryptophan relative to other amino acids can increase plasma tryptophan and brain serotonin levels.
The timing of meals, including those close to bedtime, has been a topic of interest in weight management studies. Contrary to some popular beliefs, several well-designed investigations indicate that the total daily caloric intake and macronutrient distribution are more significant factors in weight regulation than the timing of meals.
The body’s internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, influences metabolism. Although some studies have suggested that consuming a large meal right before bedtime may slightly alter metabolic processes, the overall impact on weight gain or loss seems to be limited when considering the whole day’s eating habits.
Digestion is an intricate process that involves various physiological mechanisms. It’s well-established that our digestive system continues to function while we sleep, although at a slower pace. Contrary to common misconceptions, digestion does not entirely shut down at night, making late-night eating a feasible option for some individuals.
Get Welltory
for better sleep
Get Welltory
for better sleep
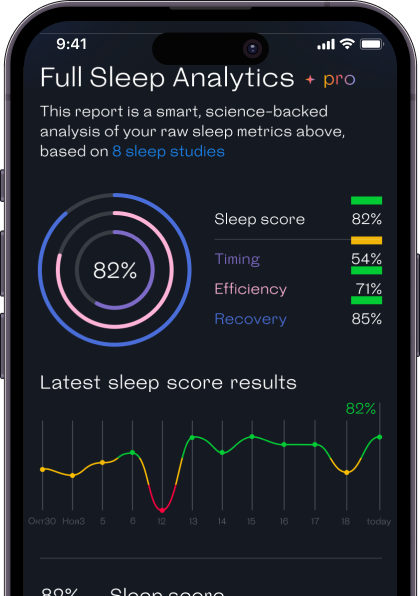
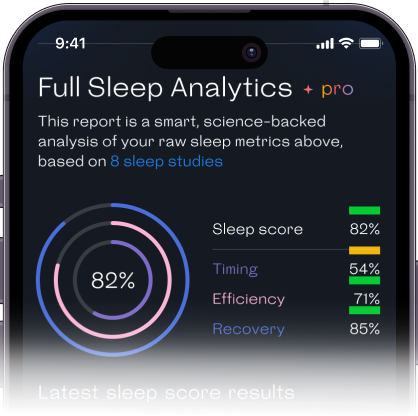

Certain foods contain compounds that can assist in digestion when consumed before bedtime. For example, herbal teas like chamomile and peppermint have soothing properties that can promote relaxation and aid digestion. Additionally, small portions of easily digestible snacks, such as yogurt or whole-grain crackers, might not negatively affect sleep or digestion.
For some individuals, eating before bed can exacerbate acid reflux and heartburn symptoms. Foods high in fat and acidity are often the culprits. If you experience these issues, it’s essential to identify trigger foods and avoid them before bedtime.
Late-night snacking, particularly on high-carbohydrate and sugary foods, may lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels. For individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, this can be particularly problematic. A 2011 study found that late-night eating, especially heavy meals, might impair glucose tolerance compared to eating earlier in the day. Impaired glucose tolerance can lead to higher blood sugar levels after a meal.
What’s even more fascinating is that shift workers, who often eat at atypical times, including late at night, are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This suggests that the timing of food intake can influence blood sugar control and metabolic health.
In conclusion, the relationship between eating before bed and its effects on sleep, digestion, and weight management is complex and varies from person to person. While some individuals may experience disruptions in sleep or digestion due to late-night eating, others may find it beneficial for promoting relaxation and supporting specific health goals. It is essential to consider individual preferences, dietary habits, and health conditions when deciding whether to indulge in a late-night snack.
As with any dietary choice, moderation and balance are key to maintaining overall health and well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian if you have specific concerns or health conditions that may be influenced by late-night eating.
Welltory Team, 23 July. 2023
 App Store
App Store
 Google Play
Google Play
 Huawei AppGallery
Huawei AppGallery
 Galaxy Store
Galaxy Store

