


Welltory is the Ultimate HRV App





The human body is a complex system that requires rest and recovery to maintain optimal health. Sleep is an essential part of our daily routine, it helps our body to recover from daily wear and tear.
When we sleep, our body undergoes several physiological changes that aid in the repair and recovery of damaged tissues. These changes are necessary for muscle recovery, especially after a workout or an injury. Lack of sleep can result in decreased muscle recovery and slow down the healing process.
When we sleep, the body releases hormones such as growth hormone, which is crucial for muscle repair and recovery. The amount and quality of sleep one gets directly impact the body’s recovery process. Getting an adequate amount of sleep allows the body to repair tissues, remove metabolic waste, and replenish energy stores needed for the next day’s activities.
Research has found that sleep disturbances, such as insomnia, can negatively impact athletic performance. A study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that athletes who slept more than eight hours a night had a better recovery rate than those who slept for less than six hours.
Another study published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology investigated the effects of sleep deprivation on muscular endurance and strength in a group of healthy adults. The study found that sleep deprivation impaired both muscular endurance and strength, with participants performing fewer repetitions and lifting less weight compared to when they were well-rested.
Sleep plays a crucial role in building muscle. This is when our bodies undergo restorative and regenerative processes, including muscle repair and growth. During sleep, the body releases growth hormone, which is essential for muscle growth, and also allows for protein synthesis.
Protein synthesis is a complex process that involves the creation of new proteins from amino acids, the building blocks of protein. Protein synthesis is essential for repairing and rebuilding muscle tissue that has been damaged during exercise. During this process, the body uses amino acids from protein sources to create new muscle proteins, which are then integrated into the muscle fibers to strengthen and enlarge them. The process of protein synthesis is regulated by a complex network of signaling pathways and hormones, including insulin, growth hormone, and testosterone, which work together to stimulate muscle growth and repair. Ultimately, protein synthesis is essential for muscle building and recovery, and optimizing this process through proper nutrition and rest is key to achieving optimal results.
One study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that sleep deprivation resulted in reduced protein synthesis rates and increased protein breakdown rates in healthy young men, leading to a net loss of muscle mass over time. Research has also found that acute sleep deprivation reduced muscle protein synthesis by 18%, increased plasma cortisol by 21%, and decreased plasma testosterone by 24%.
In addition, sleep deprivation can lead to a decrease in testosterone levels, which can further hinder muscle growth. As you know, testosterone is essential for your muscle and adequate sleep has been shown to increase testosterone levels and promote muscle recovery, making it an important factor to consider for individuals looking to maximize their muscle-building potential.
Both the quality and quantity of sleep can impact muscle building. One study found that individuals who slept for only four hours per night had reduced muscle-building capabilities and reduced muscle strength compared to those who slept for eight hours per night.
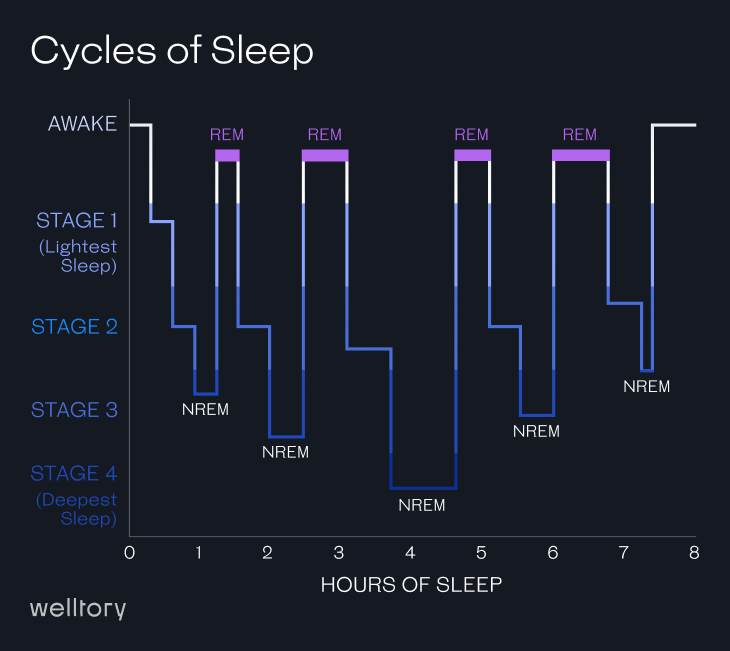
The stage of sleep during which muscles recover is primarily the slow-wave sleep (SWS) stage, also known as deep sleep. During SWS, the body experiences an increase in growth hormone secretion, which stimulates tissue growth and repair, including the repair of muscle tissue. Blood flow to muscles increases during deep sleep, allowing for increased delivery of oxygen and nutrients to promote muscle recovery.
It is worth noting that while SWS is the primary stage of sleep for muscle recovery, other stages of sleep, such as rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, also play a role in recovery and growth. REM sleep also helps to replenish glycogen stores in the muscles, which can help to improve muscle recovery and reduce the risk of muscle damage during subsequent workouts.
Get Welltory
for better sleep
Get Welltory
for better sleep

Sleep is vital in the replenishment of muscle glycogen stores. Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate that is stored in the muscles and liver, and it is the primary energy source for muscles during high-intensity exercise. During exercise, glycogen stores are depleted, and they need to be replenished to support muscle recovery and performance.
During deep sleep, the body releases growth hormone, which triggers the release of glucose from the liver, which is stored as glycogen in the muscles. This replenishment of glycogen stores is essential for maintaining high-intensity exercise performance. Glycogen is a form of glucose that the body stores in muscles and the liver, which provides energy during physical activity. When glycogen stores become depleted, muscle fatigue and weakness can occur.
Research has shown that sleep helps to enhance the rate of glycogen synthesis, which is the process of replenishing glycogen stores in the muscles. Sleep deprivation may reduce muscle glycogen synthesis rates by up to 30%. This suggests that sleep deprivation can have a negative impact on physical performance due to decreased muscle glycogen stores. Therefore, to optimize performance and recovery, athletes and individuals who engage in high-intensity physical activities should prioritize sleep.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to injury or infection, which triggers the release of cytokines and other molecules that promote healing and repair. In the context of muscle growth and recovery, inflammation can play a complex role.
On the one hand, some degree of inflammation is necessary for muscle growth and repair. When you engage in intense exercise, you create micro-tears in your muscle fibers, which trigger an inflammatory response. This response helps to clear away damaged tissue and activate satellite cells, which are important for muscle repair and growth. The resulting inflammation can cause soreness and discomfort, but it ultimately leads to muscle growth and improved function.
However, excessive or prolonged inflammation can actually impair muscle growth and recovery. This can occur if the inflammatory response is too intense or if it persists for too long. In these cases, the inflammatory molecules can interfere with the activity of satellite cells and promote the breakdown of muscle tissue, leading to delayed recovery and decreased muscle growth. Research shows that adequate sleep can reduce inflammation levels, leading to faster recovery and reduced muscle soreness.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that sleep deprivation increased inflammation markers in the body, which can lead to impaired muscle recovery and decreased exercise performance.
It is important to prioritize good quality sleep and ensure that you are getting enough restful sleep to support your body’s natural healing and recovery processes and reduce the risk of muscle strains. Evaluating the quality of your sleep is essential for ensuring adequate muscle recovery.
Some indicators of poor sleep quality include difficulty falling or staying asleep, frequent waking during the night, and waking up feeling tired. It is recommended that adults get at least 7-9 hours of sleep per night to promote optimal health and recovery.
There are several ways to assess the quality of your sleep, including the duration, the number of awakenings, and the level of deep sleep. We recommend Welltory users evaluate the quality of their sleep by using a sleep tracker and analyzing their heart rate variability.
The amount of sleep needed to recover from an injury can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the injury. However, adults generally need 7-9 hours of sleep per night. It’s important to listen to your body and get enough sleep to ensure proper recovery and healing.
Yes, sleep deprivation can delay muscle recovery. When we don’t get enough sleep, our bodies are not able to repair and regenerate as effectively. This can lead to a slower recovery time, increased risk of injury, and reduced muscle growth. Additionally, sleep deprivation can lead to an increase in inflammation, which can further delay recovery.
Yes, poor sleep quality can lead to muscle soreness. When we don’t get enough quality sleep, our bodies are not able to repair and regenerate as effectively. This can lead to muscle soreness and a slower recovery time. Additionally, poor sleep quality can lead to an increase in inflammation, which can further contribute to muscle soreness.
While there is limited research on the specific effects of sleep positions on muscle recovery, it is generally recommended to avoid sleeping on the affected muscle or injury as it may cause further discomfort or even pain. Additionally, sleeping in a position that allows you to maintain good spinal alignment can aid in overall muscle recovery and prevent further pain.
Taking a nap can help muscle recovery by providing additional time for the body to repair and regenerate. A nap of 20-30 minutes can be enough to provide a boost of energy and mental focus, but it is important not to nap too close to bedtime as it may affect your nighttime sleep quality. It’s also important to listen to your body and take a nap if you feel tired or fatigued.
Welltory Team, 22 Feb. 2023
 App Store
App Store
 Google Play
Google Play
 Huawei AppGallery
Huawei AppGallery
 Galaxy Store
Galaxy Store

