Desk job and your health
Scientists have found out that ergonomic office desks and chairs help to improve overall health, boost productivity and increase concentration. Find out how you can improve your workplace.

Being happy makes you more successful. It boosts your productivity and makes you healthier.
Recent discoveries in psychology, neuroscience, and management studies have shown that happiness is a precursor to success.
The Harvard Business Review, for example, has published an analysis of hundreds of studies that shows happiness increases sales by 37% and productivity by 31%. Moreover, happy employees are nearly 10 times more engaged at work and 40% more likely to receive a promotion.
When we’re happy, we become more engaged, creative, energetic, resilient, and productive. Brazilian researchers Natasha Fogaça and Francisco Antônio Coelho have found that unhappy people are more likely to take time off, have trouble concentrating, and work slowly.
Studies show that people who consider themselves happy are 22% less likely to develop cardiovascular disease. A 2006 study made by the University of Pittsburgh Department of Psychology showed that happiness improves your immune system: people who self-identified as happy produced twice as many antibodies in response to the hepatitis B vaccine.
Happiness is a persistent condition that we experience at times when we are joyful and have no negative feelings or emotions. At the same time, it’s a complicated process that occurs in the brain, where neurotransmitters produce emotions and pleasant “happiness” feelings. Various situations determine the release of these neurotransmitters and lead to the feeling of happiness.
Both.
For example, if you start exercising, your brain will recognize this as a moment of stress. As your heart pressure increases, the brain thinks you are either fighting or fleeing an enemy. Signals go to the limbic system, which is located in the central area of brain. It interacts with the frontal lobes and plays the primary role in identifying the form of emotions. Endorphins released at this moment tend to minimize the discomfort of exercise and block the feeling of pain, plus they are associated with a feeling of euphoria.
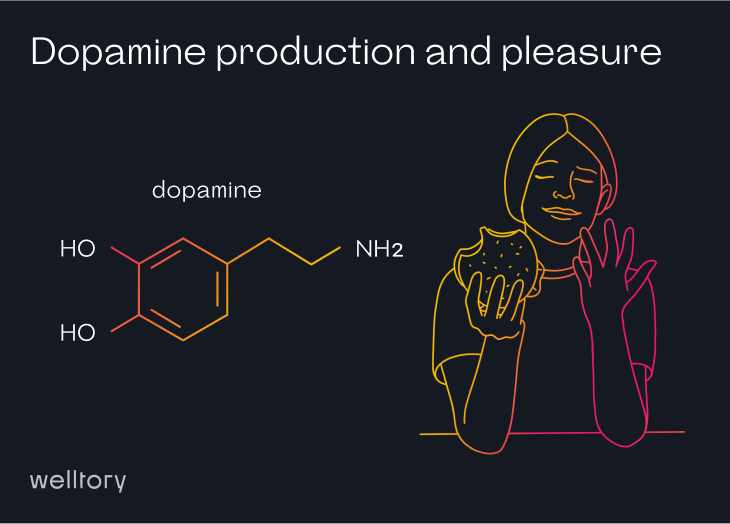
When we set a goal and achieve some kind of reward – such as satisfying hunger and thirst, winning a game, traveling, or waiting for something new – the level of dopamine transmission is increased. Dopamine is also involved in pleasure-related cognition. We learn that things like sex, enjoyable food or video games are pleasurable and try to repeat them, which may lead to addiction.
Hugs (even hugging a pet), volunteering, close friends, massages, and sex – all these actions increase oxytocin level. Oxytocin is a hormone directly linked to human bonding and increasing trust and loyalty. It also plays a role in sexual reproduction and during and after childbirth. A study conducted by Inna Schneiderman showed that high levels of oxytocin have been correlated with romantic attachment. New lovers had substantially higher plasma levels of oxytocin as compared to unattached singles. These high hormonal levels were individually stable and showed no decrease during the first nine months of successful pair-bonding.
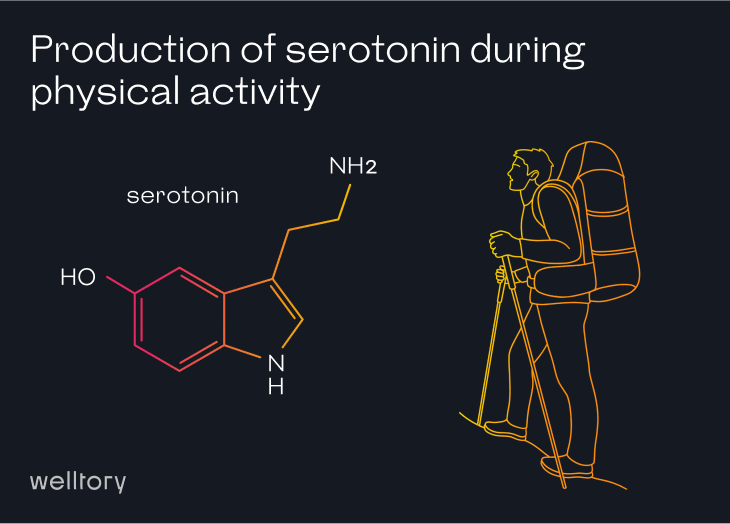
The main happiness neurotransmitter serotonin, which mediates satisfaction and optimism is mostly released in intestines (95%). If we eat food rich in tryptophan – like turkey, milk, nuts, beans, or fish – its level increase. Serotonin levels also depend on sunlight, physical activity, vitamin D, and sleep. Reduced serotonin levels cause bad moods, depression, and sleep disturbances.
Psychological studies have shown that subjective happiness can be measured reliably. Objective methods of visualization showed the precuneus zone in the brain mediates subjective happiness by integrating the emotional and cognitive components of happiness. Other brain zones involved in both higher level thought and emotion are frontal lobes. The left prefrontal cortex is more active when people feel happy and the right side of the frontal lobe – the right prefrontal cortex is more active when people feel sad. This fact suggests that our thoughts and actions affect the way we feel and vice versa.

Our happiness level is a result of a complex interaction of genes, behaviors, and what’s going on in our lives at a specific moment in time, according to twin studies made by Department of Biological Psychology, Amsterdam. There are even gender differences, resulting in a lower rate for women and a higher one for men (22% and 41%). This is a basic level of happiness that we often realise only after a loss or victory.
We can train ourselves to become happier changing happiness-relevant circumstantial factors, and happiness-relevant activities and practices. So we have the ability to offset our genetic level of happiness, which brings us to the most important takeaway from the scientific research. This leaves as much as 50% and more of the variance for intentional activity. Recent research into the types of interventions designed to promote positive emotional qualities suggests that such qualities may be the product of skills we can learn through training — in the same way that practice improves our musical or athletic abilities. In other words, changing our intentional activities may provide a happiness-boosting potential larger than our fixed circumstances.
You have the power to take control of your happiness by choosing your thoughts, behaviors, and actions. Over time, we can build lasting habits that increase our resilience and improve our happiness levels.
Researchers investigated the idea that people seem to have a fundamental need for close social relationships. The happiest individuals without exception reported strongly positive social relationships.
No, it’s not. There is a difference between happiness and pleasure.
Pleasure is a momentary feeling that comes from something external — a good meal, a massage, making love, and so on.
Pleasure has to do with the positive experiences of our senses, and with good things happening. Morten L. Kringelbach and Kent C. Berridge (University of Oxford) argue that pleasurable experiences can give us momentary feelings of happiness, but this happiness does not last long because it is dependent upon external events and experiences.
We have to keep on having the good experiences — more food, more drugs or alcohol, more money, more sex, more things — in order to feel pleasure. As a result many people become addicted to these external experiences, needing more and more to feel a short-lived feeling of happiness. Happiness, yes, includes pleasure, but it doesn’t consist only of pleasure.
To be happy, people need something more: strong relationships, doing good things for other people. Striving for pleasure we don’t always reach the destination of “happiness.” But as we said before, some of the activities that bring us pleasure can also increase our basic level of happiness.
Of course! Especially when you spend a great deal of your life working, and the World Happiness Report 2017 proves it. Every job can bring you happiness if you love it. Jose Mourinho once said: “For me the most important thing in my life is love… If you are not in love with your job, you must change your job.”
Understanding your personality traits helps you recognise which working environments you are best suited to. People are happy when they use skills that make them feel energised.
According to the recent report from CareerBliss including 25,000 respondents, the happiest job is a marketing specialist. The main advantage of this job is the ability to exercise creativity and problem-solving in their task of building out a company’s marketing strategies. This evaluation gauged an employee’s relationship with their boss and co-workers, the work environment, job resources, compensation, growth opportunities, company culture, company reputation, daily tasks, and control over the work performed on a daily basis.
According to a Gallup World Poll tracking people working blue-collar jobs, they report lower levels of overall happiness in every region around the world. White-collar workers generally report experiencing more positive emotional states such as smiling, laughing, enjoyment, and fewer negative ones like feelings of worry, stress, sadness, and anger.
People around the world who categorize themselves as a manager, executive, official, or professional worker evaluate the quality of their lives at a little over 6 out of 10, whereas people working in farming, fishing, or forestry evaluate their lives around 4.5 out of 10 on average. Global averages let us see that self-employment is generally associated with lower levels of happiness as compared to being a full-time employee. Being self-employed is associated both with higher overall life evaluation and with more negative daily emotions such as stress and worry. Everyone who owns a business knows that being self-employed can be both rewarding and stressful.

The self-employed often suffer from the following causes of stress:
All of these factors can turn your dream into a nightmare.
Not necessarily. We might think a six figure salary will make us happier but this is not exactly the case. Receiving a raise at work, buying a new car, or winning the lottery are not usually the road to long-term happiness. Over time good things and bad things usually lose their power to strongly affect us. Many of the good and bad events provide only short ups and downs.
People with a higher income have less job satisfaction according to English researchers. Another study conducted by the European Social Survey says that people in well-paying jobs are happier and more satisfied with their lives and jobs. The point is that money increases happiness only when it helps to pull people out of poverty. A large body of research has shown that the non-monetary aspects of employment are key drivers of people’s wellbeing – fresh involvement in activities, relationships, and goals can be a continuous source of happiness.
No, it won’t help you be happier. The quality of one’s friendships, not their quantity, makes a difference in personal happiness. The overall number of friends reflects the sociability and likeability of the individual. Relationships, especially friendships, play an integral part in our everyday life.
Friendships are an important source of happiness. Being alone rates the lowest levels of happiness, while being with a friend corresponds to the highest. Scientists discovered that friendship variables account for 58% of variance in happiness. So do things with your friends, share your thoughts and ideas with them to increase your happiness level to a maximum.
Yes and no. Having a strong marriage may make us happy. Expert in happiness Sonja Lyubomirsky says that happy people have more chances to attract a marriage partner and to build an enduring and fulfilling partnership.
A Harvard Study of Adult Development has shown that married people are mostly happier than other groups (single, divorced, widowed). Happiness in marriage consists of many factors which are associated with happiness: intimacy, children, domestic and financial support, companionship in old age.
For example, having sex one additional time per week increases likeliness of being very happy in a marriage by 7.7% for women and 5.4% for men. Another important factor is one’s satisfaction with marriage and family life, which is the strongest correlate of happiness.
Being married doesn’t necessarily lead people to experience more happiness from moment to moment. For example having a child reduces happiness on average by 0.24%. Married women spend less time with friends, less time reading or watching TV, and more time doing chores, preparing food, and looking after children.
So you can increase your happiness level by marriage if you maintain warm close interpersonal relationships with a spouse, friends and relatives.

In theory you can, but real life is much harder. Even very happy people by all measures experience distress, sadness, frustration, anger, etc. The very idea that one should be happy all the time makes you more unhappy, not less so, because the contrast is too great between how things are and how they should be.
Get rid of the idea that you should be happy all the time. This puts an enormous amount of pressure on you and makes you more unhappy. Don’t worry. You can boost your basic level of happiness.
Physical exercise. As we mentioned previously, this increases your endorphin levels and make you happier. Regular running and other aerobic physical activity not only increase longevity but can also be used as a treatment for mental health diseases including depression, anxiety and insomnia. To start, find at least 30 minutes 5 times a week for physical activity. Aerobic exercise mostly reduces stress and improves memory. Lifting weights helps in complex thinking, reasoning, multitasking, and problem solving. Yoga integrates thoughts and emotions, reduces fear and anxiety.
Sleep is important for your mental, physical and emotional wellbeing and It is really hard to be happy when you haven’t got sufficient sleep. Sleep deprivation induces alterations in goal-directed behaviors, causing us to experience negative emotions rather than positive ones. “Making $60,000 more in annual income has less of an effect on your daily happiness than getting one extra hour of sleep a night,” reported Norbert Schwarz, Phd., a professor of psychology.
Track your sleep duration and level of energy and stress to understand your own sleep needs. By going to bed at the same time each night and getting up around the same time each day, you make it easier for your body to regulate its sleep/wake cycle.
Smoking
Nicotine triggers chemical reactions in the brain that have effects similar to neurotransmitters endorphins and dopamine. They are associated with sensations of pleasure leading to addiction. It’s a common myth that smoking is actually good for your mental health because it relieves stress and aids in relaxation. It is widely believed that stopping smoking leads to an increase in mood disturbances and depressive symptoms. Nonetheless, those who stop smoking become happier than smokers after one year.
Alcohol
People drink to socialize, celebrate, and relax. A recent study confirms that drinking alcohol considerably increases your happiness level in the moment but this effect doesn’t last long. The reason is the release of endorphins and serotonin after alcohol intake. These neurotransmitters cause pleasure and relax us. Be careful: abnormal basic serotonin levels may contribute to the development of alcohol abuse.
Yes, it can. Some food can increase neurotransmitter levels.

It’s because sweets quickly increase the levels of sugar in the blood. These levels get very high after the first hour. This makes your brain feel happy for a while. After the second hour, blood sugar significantly decreases and neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin level off as well. This can lead to fatigue, mood changes, and depression.
A team led by David Ludwig, MD, PhD, director of the New Balance Foundation Obesity Prevention Center at Boston Children’s Hospital, found that consuming highly processed, rapidly digested carbohydrates can cause excess hunger and stimulate brain regions involved in rewards and cravings. It is healthier to consume food with a low glycemic index, because it doesn’t cause a sharp fluctuation of happiness hormones in your brain.
Gather data about yourself. It is important because every person is unique and there are no universal recommendations. Find something that will be suitable exactly for you. There are some applications like Happify, Live Happy, Headspace, MyMoodTracker which help you to switch your brain to positivity.
Our own feelings often differ from real data: use applications like Welltory and Rescue Time, measure your stress and energy levels, and gather data from fitness trackers. Then, you will know what makes you more productive, how much time you need for making decisions, how long you need to sleep, what foods and other factors make you feel good and truly happier, etc.
Welltory Team, 23 Dec. 2021

Scientists have found out that ergonomic office desks and chairs help to improve overall health, boost productivity and increase concentration. Find out how you can improve your workplace.

Do you often suffer from headaches? Find out what the difference between a headache and a migraine is and check for symptoms.

Find out how to track air quality, humidity and noise levels to optimize your performance and to avoid frequent colds.
Self-tracking and lifelogging is a great way to learn more about yourself so you can be healthier, happier, and more productive.
 App Store
App Store
 Google Play
Google Play
 Huawei AppGallery
Huawei AppGallery
 Galaxy Store
Galaxy Store







