Measuring Resting Heart Rate
From manual pulse counts to the latest in app technology, dive into the transformative journey of heart rate monitoring

Even if you’re blissfully unaware of what’s happening, parts of your brain and body are hard at work while you’re asleep. That’s why getting enough sleep is essential. But the amount of time you spend in bed isn’t all that matters — quality is important too. During a single night, the brain cycles through different phases, all producing specific benefits and complementing each other. Understanding and tracking these phases can help you improve your sleep and overall wellbeing.
A typical sleep cycle consists of four stages, with each stage falling into one of two categories: REM (rapid eye movement) and non-REM (NREM). NREM stages can further be divided into light and deep sleep. One full cycle that includes all four stages lasts 90 to 110 minutes, so on average, you should be completing 4 to 6 cycles during a single night.
When you drift off, you first enter non-REM sleep, which gradually progresses from light to deep over the course of an hour and a half. You then have a brief period of REM sleep that only lasts one to five minutes. But as the night goes on, you’ll experience less deep sleep and more REM, with the most prolonged REM phase just before waking.
During each phase of the sleep cycle, different parts of your body and brain are active as specific processes take place to prepare you for the day ahead.
Stage 1: The first stage of NREM sleep lasts five to 10 minutes. During this period, your body and brain begin to slow down. Your muscles may occasionally twitch, a phenomenon known as a hypnic jerk. If you wake during this stage, it might feel like you didn’t sleep at all.
Stage 2: The second stage of NREM accounts for about 50 percent of the total sleep cycle. In this phase, your eyes stop moving, muscles relax, and core body temperature decreases. Brain waves also slow down, with occasional bursts of high-frequency waves known as sleep spindles. Researchers believe these are important for committing new motor skills to memory.
Stage 3: The third phase of NREM is deep sleep. At this stage, the brain produces very slow waves, known as delta waves. Your eyes turn upward, and it’s very difficult to wake up. Breathing slows to about 15% lower than waking. Your heart rate is also slower during deep sleep vs REM – about 20 to 30% lower than when you’re awake and resting.
Stage 4: After deep sleep, the REM cycle begins. During REM, your eyes move rapidly from side to side beneath your lids, and your heart rate and breathing speed up. It is challenging to move, and your limbs may become temporarily paralyzed. Some scientists theorize this is to prevent you from acting out your dreams. During REM, brain activity is similar to when you’re awake, which is why most vivid narrative dreams occur during this stage. Because the muscles are so relaxed at this point, sleep apnea may be worse.
Deep sleep and REM sleep both have particular benefits. Without enough of either, your body and mind can’t fully recover and rejuvenate.
Most physical restoration processes occur during deep sleep.
Most physical restoration processes occur during deep sleep.
Get Welltory
for better sleep
Get Welltory
for better sleep

Just like a person’s dietary requirements change with age, the amount of REM sleep vs. deep sleep they need does too.
Because there are benefits to REM and deep sleep, ensuring you get enough of both can help you feel and perform your best each day.
While scientists use a method called polysomnography to study sleep in the lab, you can sync Welltory with a number of devices to get similarly reliable results about the quality of your sleep.
Wearable devices, like Apple Watch or Fitbit, track your heart rate, as you’ll recall, changes depending on what phase of sleep you’re in. Alternatively, you can track your sleep with apps like Sleep Cycle and Sleep as Android and see how much time you spend in different sleep stages.
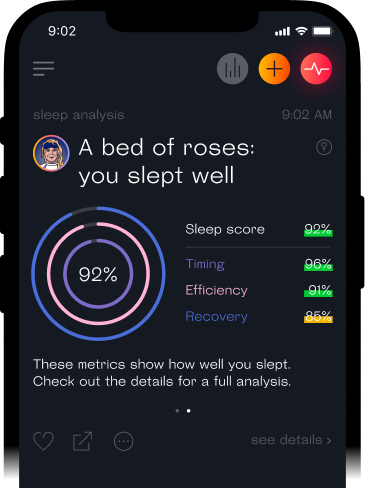
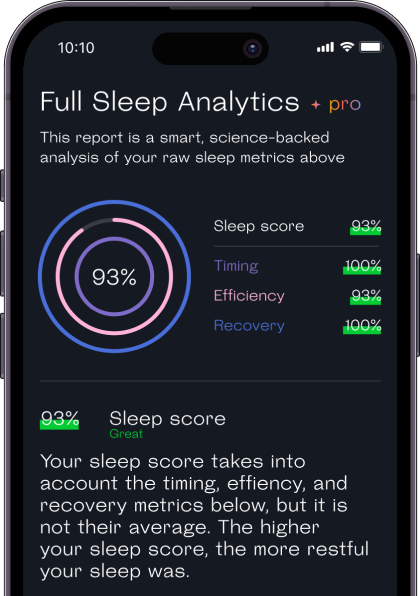
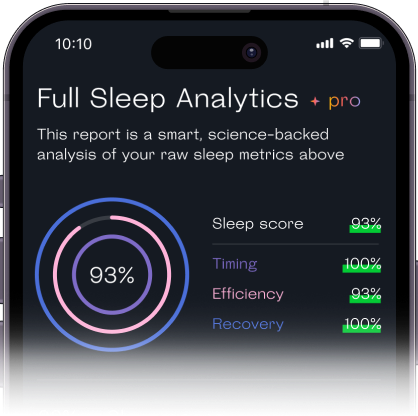
Welltory analyzes the data from these devices and apps to produce personalized insights and recommendations to help you optimize your sleep and make sure you’re getting enough REM and Deep sleep each night.
With Welltory’s sleep analysis, you’ll also get a sleep score that can show you how well you’re meeting your sleep goals every night, using parameters like how well you recovered and whether or not you’re going to bed and waking up at the best time for your needs.
Making sure you’re getting quality sleep will not just help you feel more energized the next day but will also support your body’s many systems so you can live a healthy and productive life.
Welltory Team, 12 Jan. 2023

From manual pulse counts to the latest in app technology, dive into the transformative journey of heart rate monitoring

Discover the intricate relationship between late-night eating and its impact on sleep duration and quality
From boosting cognitive function to enhancing physical performance, discover the impact of blood oxygen levels on various aspects of health

The relationship between stress and productivity and how Welltory can help you plan better

Does sleeping burn any calories, should you exercise right before bed and how much do you need to sleep to burn a 1000 Cal

All you needed to know about headaches at night – types of nighttime headaches, their causes, possible treatment and how to avoid them.
 App Store
App Store
 Google Play
Google Play
 Huawei AppGallery
Huawei AppGallery
 Galaxy Store
Galaxy Store







