


Welltory is the Ultimate HRV App




Home » Heart Rate Variability » Heart Rate by Age and Gender

We often hear about heart rate as an indicator of overall health and wellness. It’s true that our heart rates depend on a multitude of lifestyle factors, however two of the most important factors affecting the rhythm inside our chests are age and biological gender.
Heart rate can be influenced by a variety of factors, including age, gender, fitness level, medications, and other health conditions. In this article, we will cover how it differs among people of different ages and gender.
Heart rate (HR) is the number of times your heart beats in a minute. A resting heart rate (RHR) refers to the number of times your heart beats per minute when your body is at rest and is relaxed. Resting heart rate is a baseline measurement of your heart’s functioning and varies among individuals. It serves as a useful indicator of cardiovascular health and fitness level and a number between 60 and 100 beats per minute is considered normal.
Monitoring your heart rate is important for maintaining cardiovascular health and ensuring that you’re exercising at an appropriate intensity level based on your maximum heart rate.
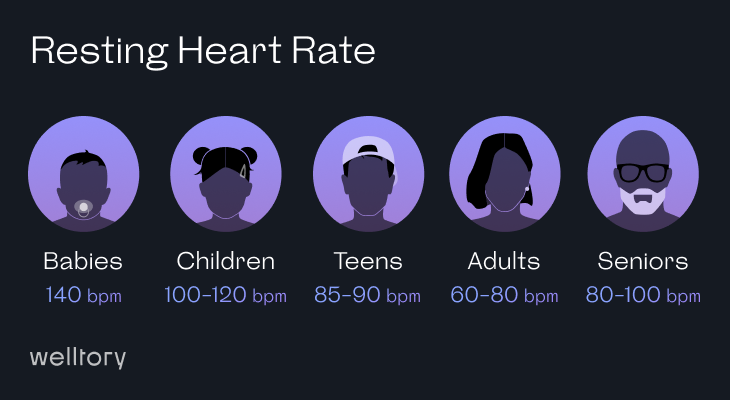
Resting heart rate tends to decrease with age as our cardiovascular system becomes more efficient, and the heart doesn’t need to work as hard to pump blood throughout the body. The normal resting heart rate for adults can range from 60 to 100 beats per minute, but the average resting heart rate for adults is usually between 60 and 80 beats per minute.
Yes, resting heart rate can differ between men and women. On average, females tend to have slightly higher resting heart rates than males, even when other factors such as age and physical fitness are taken into account. Moreover, this difference in resting heart rate between genders could be due to various factors, including hormonal differences, body composition, and more.
Studies have shown that females tend to have resting heart rates that are about 8-10 beats per minute higher on average than males. The average adult male heart rate is somewhere between 70 and 72 beats per minute, while the average for adult women is between 78 and 82 beats.
Get Welltory
to track heart rate
Get Welltory
to track heart rate
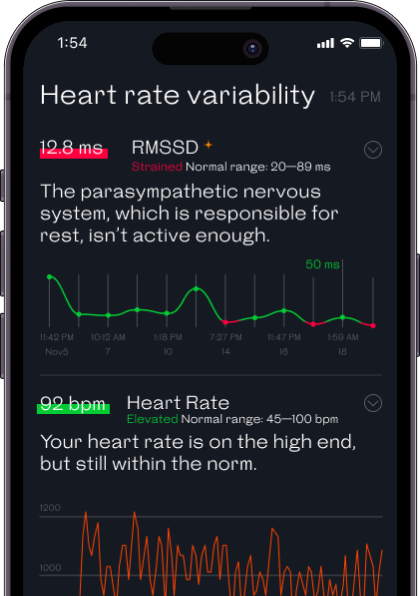

This difference can be explained by the size of the heart. Females tend to have smaller hearts than males. Pumping less blood with each beat, a smaller heart needs to beat at a faster rate to match the larger heart’s output. Moreover, research demonstrates that females have different intrinsic rhythmicity to the pacemaker of their hearts causing them to beat faster.
The natural pacemaker of the heart is called the sinoatrial (SA) node. It’s a small cluster of specialized cells located in the right atrium of the heart. The SA node generates electrical impulses that stimulate the contraction of the heart muscle and regulate the heart rate.
Research has shown that there may be differences in the intrinsic rhythmicity of the pacemaker, or the natural rate and rhythm of contraction, between males and females. This means that the pacemaker in females may have a different inherent rate of electrical activity than the pacemaker in males. Women are more likely to have an electronic pacemaker implanted for SND or atrial fibrillation with bradycardia. Moreover, various cardiovascular drugs can have different effects on men and women.
In addition to that, a study conducted on male and female fetuses concluded that the difference in their heart rates is not clinically significant. There can also be small differences in resting heart rate between male and female children. However, the differences are generally smaller than those seen in adults. It is suggested that after the age of 15, resting heart rate tends to be slightly higher in females than males because, during puberty, men’s hearts start to grow about 15% to 30% larger than women’s hearts, as their bodies grow bigger too.
Testosterone is a hormone that is primarily produced in testicles in men, but it is also present in smaller amounts in women. The complexity of heart disease and testosterone has long been an area of interest in medical research, with numerous studies evaluating the potential link between the two. Although there is no direct association between testosterone and heart disease, the fact that men have more testosterone than women and develop heart disease earlier than their female counterparts has led researchers to suspect a potential connection.
Evidence suggests that male hormones can bind to receptors in cardiac cells and cause enlargement of the heart. For example, athletes who abuse testosterone and other steroids are at a significantly higher risk of developing high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke. However, the impact of physiological levels of testosterone on cardiac health remains unclear, with conflicting reports from studies on the relationship between testosterone levels and the risk of death from coronary artery disease. While steroid abuse should be avoided for many reasons, the ongoing search for the truth about the impact of testosterone on cardiovascular health continues.
Another example of disagreement among researchers is a link between testosterone levels and coronary artery disease (CAD). Although it is believed that higher testosterone levels account for the higher burden of coronary disease in men than women, there is an increasing body of literature indicating that men with CAD have significantly lower testosterone levels than men without CAD.
Some studies have suggested that higher levels of testosterone may be associated with increased heart rate and blood pressure, particularly in men. However, the evidence on this topic is somewhat mixed, and other studies have found no significant association between testosterone levels and heart rate.
It’s also worth noting that testosterone levels can be influenced by a variety of factors, including age, body composition, physical activity, and stress levels. Therefore, it is difficult to isolate the effects of testosterone on heart rate from other factors that may be contributing to changes in cardiovascular function.
Heart rate can change throughout pregnancy, and it is influenced by a variety of factors related to changes in the cardiovascular system and metabolic demands of pregnancy.
During the first trimester of pregnancy, the heart rate may increase slightly as the body works to support the growing fetus and maintain adequate blood flow to the placenta. However, these changes are generally minor and may not be noticeable to the pregnant person.
In the second trimester, the heart rate may continue to increase as the body adapts to the increasing demands of pregnancy. This is due to the effects of hormones such as progesterone and estrogen, which can increase heart rate and cardiac output. However, the increase in heart rate during this period is generally modest, and most pregnant people are able to maintain a normal level of physical activity without difficulty.
During the third trimester, the heart rate may increase further as the body prepares for labor and delivery. This is due in part to increased levels of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, the growing fetus and uterus can place increased pressure on the diaphragm and other organs, which can affect breathing and heart rate.
Do note however, that individual differences in heart rate during pregnancy can be influenced by a variety of factors, including maternal age, body mass index, and overall health status.
Menopause too can have an effect on heart rate due to changes in hormone levels. As women go through menopause, their levels of estrogen and progesterone fall. These hormones play a role in regulating heart rate, so a decrease in their levels can lead to changes in heart rate.
Research has shown that menopausal women may experience an increase in resting heart rate, as well as changes in heart rate variability (the time between heartbeats). This increase in resting heart rate may be due to a decrease in parasympathetic nervous system activity, which helps to slow down the heart rate.
Estrogen plays a crucial role in protecting a woman’s heart arteries by reducing the buildup of fatty plaque, which increases the risk of heart and circulatory diseases in postmenopausal women. Moreover, low estrogen levels can lead to high cholesterol levels, further increasing the risk of heart and circulatory disease. Moreover, hormonal changes during menopause can cause palpitations, where an individual experiences a rapid heartbeat, sometimes occurring during hot flashes.
Regardless of age and gender, resting heart rate can be influenced by a multitude of factors, including physical fitness, body size and composition, genetics, hormones, medications, stress and anxiety, and underlying health conditions. These factors interact in complex ways, contributing to individual variations in resting heart rate. However, regardless of these influences, monitoring and understanding resting heart rate and heart rate variability can be facilitated through tools like Welltory App.
Understanding you hear rate acts as a guideline that can tell you how hard you’re working, to what extent you can increase the intensity of your workout and further and when it’s better to loosen the pressure and stop pushing yourself too hard, which can be damaging for your health.
Welltory is a monitoring app that tracks and analyzes heart rate and heart rate variability by keeping track of your body’s current state, general fitness, and activity level. Our algorithm also takes into account additional data such as your step count, your mood, sleep, and more; we evaluate your goals and provide personalized recommendations to help you optimize your lifestyle their heart rate and maintain a healthy cardiovascular system regardless of your age or gender.
Welltory Team, 17 May. 2023
 App Store
App Store
 Google Play
Google Play
 Huawei AppGallery
Huawei AppGallery
 Galaxy Store
Galaxy Store

