The science of happiness
Happiness depends on a number of things: genes, habits, and what’s going on in our lives at a specific moment in time. Here’s what you can do to be happier.

Yes. The main reasons are lack of physical activity and a poorly organized workplace. Sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes, and is one of the main reasons for obesity and premature death in people over 40.
Poor workplace ergonomics is just as bad. Keeping the same position for too long restricts blood circulation and you start feeling sleepy, tired, lose concentration, and cannot get things done. It also causes back, neck and shoulder pain, stiffness in wrists and fingers, headaches, and vision problems.
To avoid negative effects, make sure you:
Scientists from the University of New Hampshire proved that proper workplace ergonomics has a lot of health benefits. Another study showed that ergonomic desks and chairs combined with good posture improve overall health, productivity, and concentration.
They need to be fully adjustable to your body’s dimensions. Adjustable chairs prevent back strain, while desks and armrests of the right height ensure proper shoulder position.
A good sitting desk is:
A good standing desk is:

A good office chair:
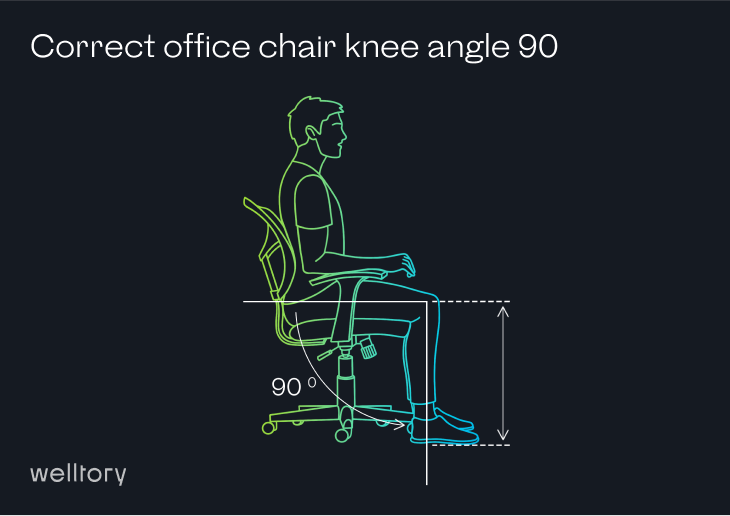
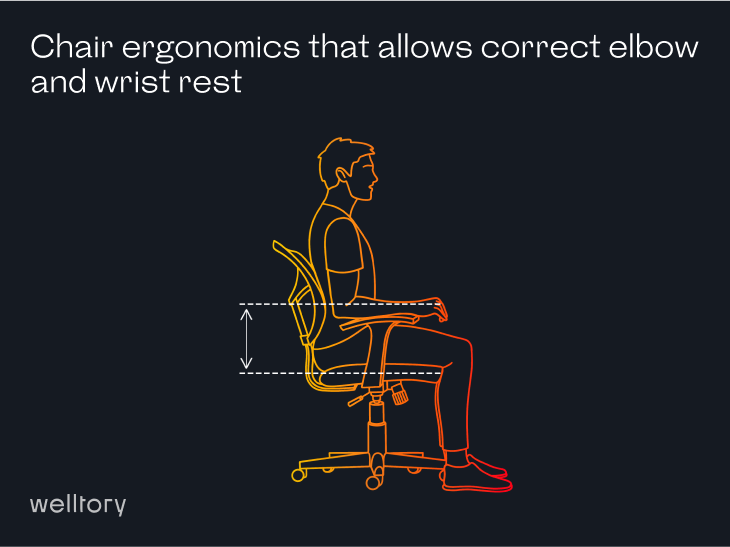
What if I have a different chair?
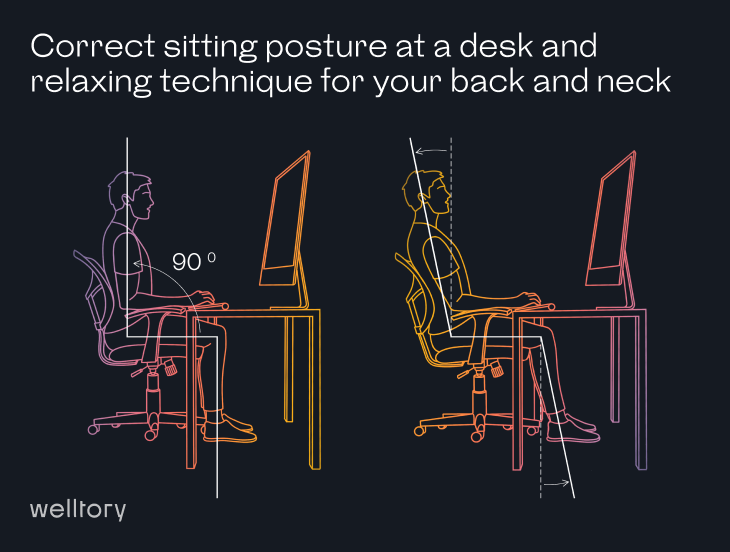
Probably check your posture. Here are some basic rules:
For legs and thighs:
For shoulders and arms:
Pay attention to the height. A screen placed too high or too low forces a forward head posture and leads to headaches, neck spasms, and shoulder strain. To avoid it:
What if I work on my laptop?
The same rules apply here.
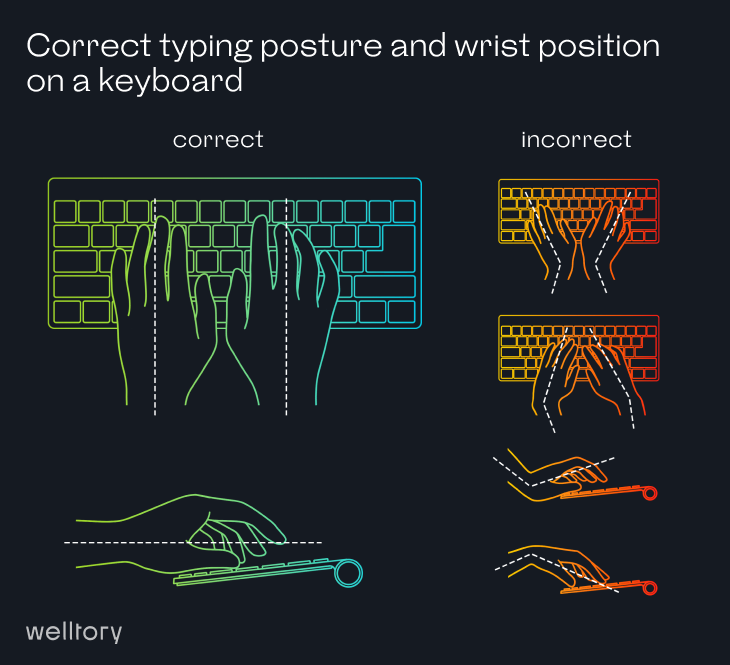
What about the mouse and keyboard?
Positioning your mouse and keyboard in the wrong way causes wrist pain.
To avoid it:
Natural light will do the trick. Office lighting affects our mood and wellbeing. Bad lighting is known to cause eye strain, headaches, and fatigue.
Research that dates back to as early as 1979 shows that exposure to natural light lowers stress, improving mood and concentration. And in 2014 scientists from the Northwestern University proved that it also improves sleep and overall quality of life. Natural light increases serotonin levels, which leaves you feeling happy, calm, and focused.
So, if possible, choose an office with larger windows that get a lot of sunshine. Or at least make the most out of what you have:

Depends on your preferences and what you are working on. Several studies have linked listening to music with increased productivity and overall wellbeing.
Listening to music at work can help you:
In other words, feel free to turn on some music while working. Just make sure you choose the right kind to help you boost performance, increase concentration and work more efficiently.
Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety recommends combining daylight ceiling light and desk lamps to lower strain on the eyes. Ceiling lamps light up large areas but should not be too bright to ensure you can still see the screen well.
When it is dark outside, turn on the desk lamp as well to avoid the contrast between a brighter screen and a darker room. If you do not have a desk lamp, turn on night shift on your computer and the screen will start emitting a gentler, warmer light.
Experts also recommend metal-halide bulbs, which are 80% identical to the natural light. Blue-enriched light bulbs have been proven to increase concentration and are great for office spaces. Warmer tones, on the other hand, help to relax and rest so they are a better fit for break rooms.

Yes. A research by the University of Minnesota proved that a clean and organized workplace motivates people to do what is expected of them in other areas as well: eat healthier, work out regularly, and give to charity. When asked if they were willing to donate money, 82% of the participants who completed the questionnaire in a cleanroom said yes, while only 47% of those who did it in an unkempt room agreed to do so.
On the other hand, a cluttered desk has been connected to thinking more creatively and generating more new ideas.
If you decided to declutter your desk, here is how you do it:
Matt Perman recommends in his book How to Set Up Your Desk to first put all the things that require your attention on the left side of the desk. Once you are done, move them to the right side. That way you’ll always be able to see what you need to get done and keep your desk clean.
Take breaks and change your position every 30 minutes or do a little warm-up routine:
When working on a computer you need to relax your eyes. Do these exercises every 20 minutes to improve blood circulation and relax eye muscles:
Sure. The main rules are:
Keep your posture:
Create the right office environment:
Take breaks every 30 minutes:
Remember the figures:
Welltory Team, 23 Dec. 2021

Happiness depends on a number of things: genes, habits, and what’s going on in our lives at a specific moment in time. Here’s what you can do to be happier.

Do you often suffer from headaches? Find out what the difference between a headache and a migraine is and check for symptoms.

Find out how to track air quality, humidity and noise levels to optimize your performance and to avoid frequent colds.
Self-tracking and lifelogging is a great way to learn more about yourself so you can be healthier, happier, and more productive.
 App Store
App Store
 Google Play
Google Play
 Huawei AppGallery
Huawei AppGallery
 Galaxy Store
Galaxy Store







